Special Education Teacher Resources
How do I find out which of my students have an IEP or a 504? How do I see their documentation?
Considerations for Special Education During Distance Learning
Considerations mentioned in our Distance Learning Plan:
- Educators must adhere to IEP just as they always would in a brick and mortar setting.
- Educators will attend IEPs.
- Focus on ensuring equity and accessibility for all students. In addition to accommodations listed in students' IEPs, focus on best practices regarding accessibility of content when designing emote learning experiences. Please see below "Accessibility During Distance Learning" for specifics.
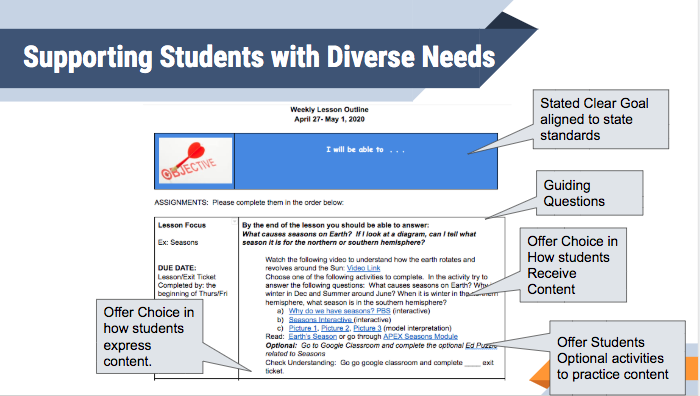
- Plan for special education students in you classroom by: including parents (request feedback, input) when your plan instruction. Focus on collaborating (special education and general education working together). Special education teachers can assist with accommodations/modifications of services and/or lessons. General education lessons can be recorded so students can have access to repeat lessons. When considering what practices should be implemented for your classroom, please refer see below heading The Implementation Do's and Don'ts of Special Education Services During Distance Learning
- Universal Design for Learning: ensure access and removal of barriers for learning for ALL Students. See Below for UDL During Distance Learning
It is critical to ensure the accessibility of resources for all students. In particularly, when considering students with individualized education programs (IEPs) or 504 plans. Here are some things that can hep support our diverse learners:
- Use Heading styles that will allow screen reader software to navigate from section to section. For Google Docs go to "Normal Text" and change the title to Heading 1, Heading 2, . . .

- Use font, size, and text formatting to distinguish between items or to navigate. Ensure no information is conveyed solely buy color or sound. See Examples Below:
| What NOT to do | DO |
|
X Keep the heading the same size/font
 |
√ Headings with different sizes and fonts than body text
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
- Use Alt-Text to allow users with screen readers or with slow connections to identify your images, graphs, and charts
| How do I add Edit or Add Alt-Text? |
 Directions:
1) Select an image, drawing, or graphic
2) Right click Alt text
3) Enter a title and description
4) Click Ok or
Youtube instructions (for other ways)
|
| When writing a description what should be considered? |
 |
- Provide transcripts of videos or audio announcements made by teachers. If you read from a script, your script should be posted as the transcript.
| Youtube: How to create a Transcript |
1. Click on the More button below the video and select Transcript from the menu.
2. Below you'll be asked to select a language. Make your choice and you'll see a full transcript along with timestamps.
3. Now click and drag to highlight all the text and press Ctrl + C to copy the text. Then paste Ctrl + V into another document to share with your students.
|
| Other ways to transcribe: | Transcribe Videos |
- If linking to external videos, make sure the videos have closed captioning available.
- Use descriptive titles, headers and subtitles to provide added context
- Use meaningful text in links to make it easier for users to predict where navigation will take them.

- Provide a balance of text, image, video,, and audio. Instruction and resources provided in more than one format provides broader support for the greatest number of users.

- Teachers should verify that the external resources they link to have the accessibility features.
- If student has real-time translation services such as CART, you may ask them to type in contents in real time while delivering lessons.
Implementation of Special Educational Services During Distance Learning
| Do's | DONT's |
|
|
Considerations for Assessments